
|
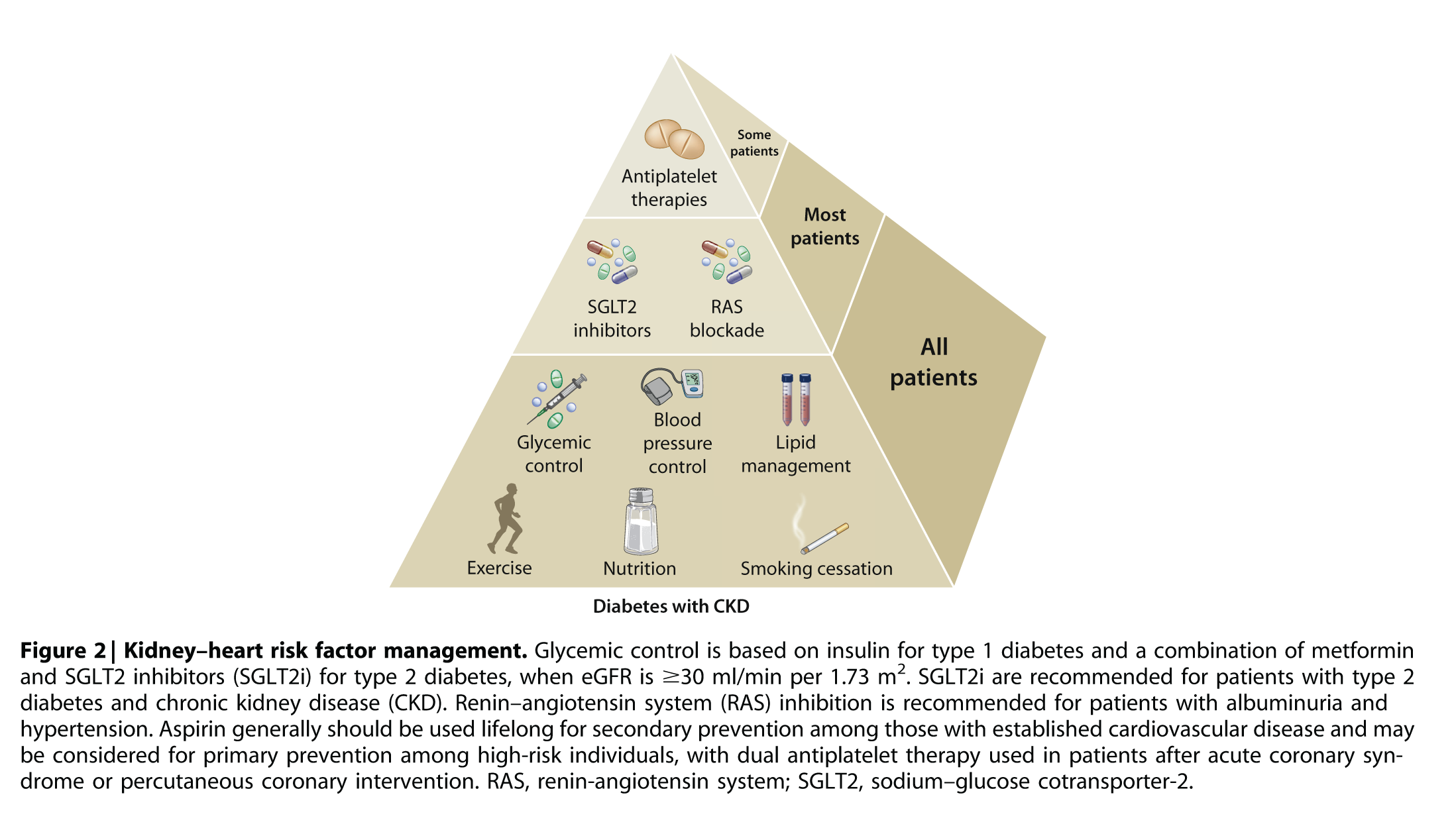
Diabetes in CKD: Visual Guidelines |
4. ANTIHYPERGLYCEMIC THERAPIES IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES (T2D) AND CKD
Practice Point 4.1:
Glycemic management for patients with type 2 diabetes and CKD should include lifestyle therapy, first-line treatment with metformin and an SGLT2i, and additional drug therapy as needed for glycemic control
3.2 PHYSICAL ACTIVITY & WEIGHT LOSS
Recommendation 3.2.1:
We recommend that patients with diabetes and CKD be advised to undertake moderate-intensity physical activity for a cumulative duration of at least 150 minutes per week, or to a level compatible with their cardiovascular and physical
tolerance (1D).
Please click here to view the 'Physical Activity' flow chart
3.1. NUTRITION INTAKE
Practice Point 3.1.1:
Patients with diabetes and CKD should consume an individualized diet high in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, fiber, legumes, plant-based proteins, unsaturated fats, and nuts; and lower in processed meats, refined carbohydrates, and sweetened beverages.
Recommendation 3.1.1:
We suggest maintaining protein intake of 0.8 g protein/kg (weight)/d for those with diabetes and CKD not treated with dialysis (2C).
Practice Point 3.1.2:
Patients treated with hemodialysis, and particularly peritoneal dialysis, should consume between 1.0 and 1.2 g protein/kg (weight)/d.
Recommendation 3.1.2:
We suggest that sodium intake be <2 g of sodium per day (or <90 mmol of sodium per day, or <5 g of sodium chloride per day) in patients with diabetes and CKD (2C).
1.3. SMOKING CESSATION
Recommendation 1.3.1:
We recommend advising patients with diabetes and CKD who use tobacco to quit using tobacco products (1D).
Please click here to view the 'Smoking Cessation' flow chart
1.2. RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN SYSTEM (RAS) BLOCKADE
Recommendation 1.2.1:
We recommend that treatment with an ACEi or an ARB be initiated in patients with diabetes, hypertension, and albuminuria, and that these medications be titrated to the highest approved dose that is tolerated (1B).
Please click here to view the 'Renin-angiotensin system (RAS) Blockade' flow chart
Please click here to view the KDIGO Blood Pressure Guideline.
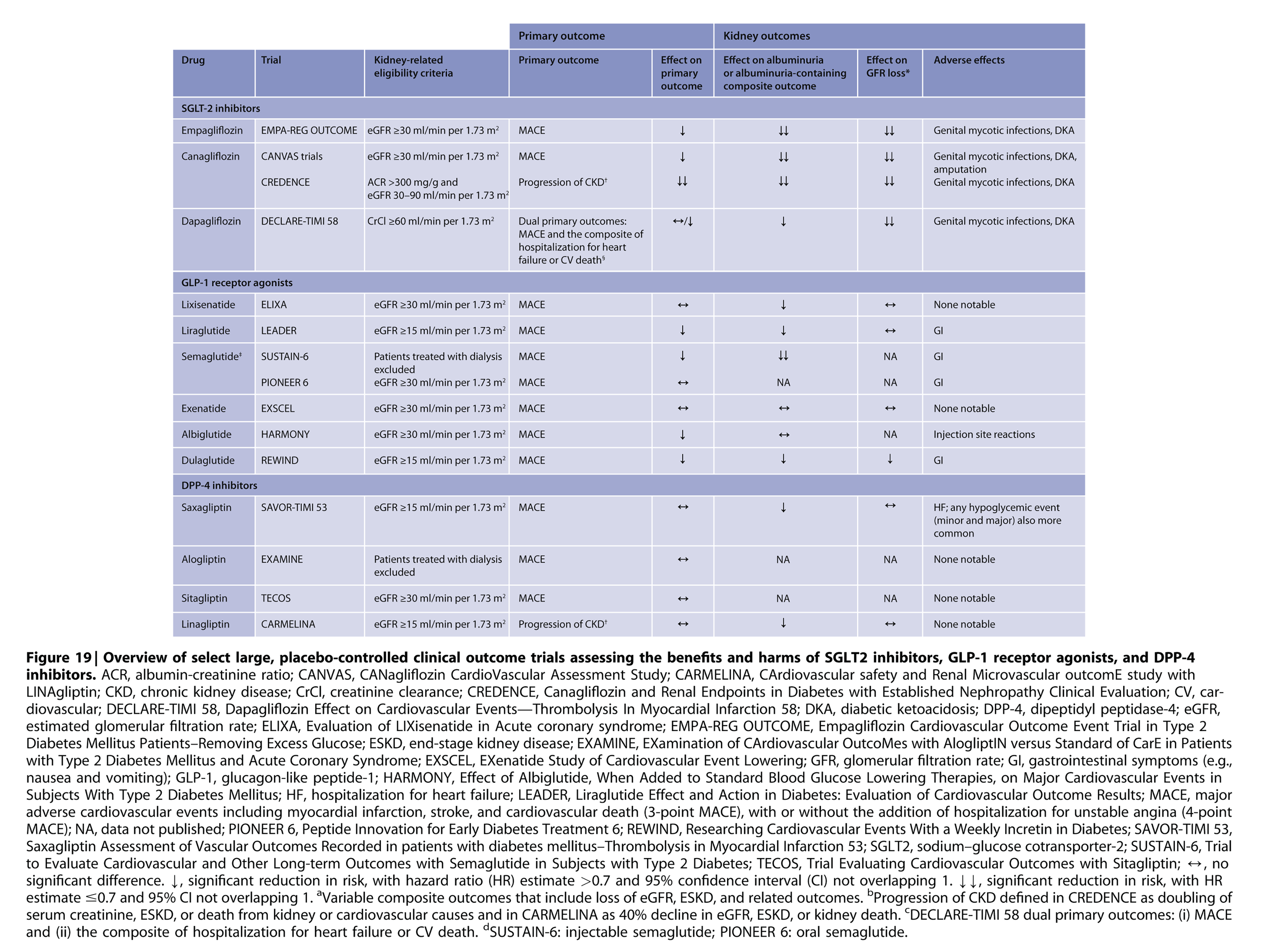
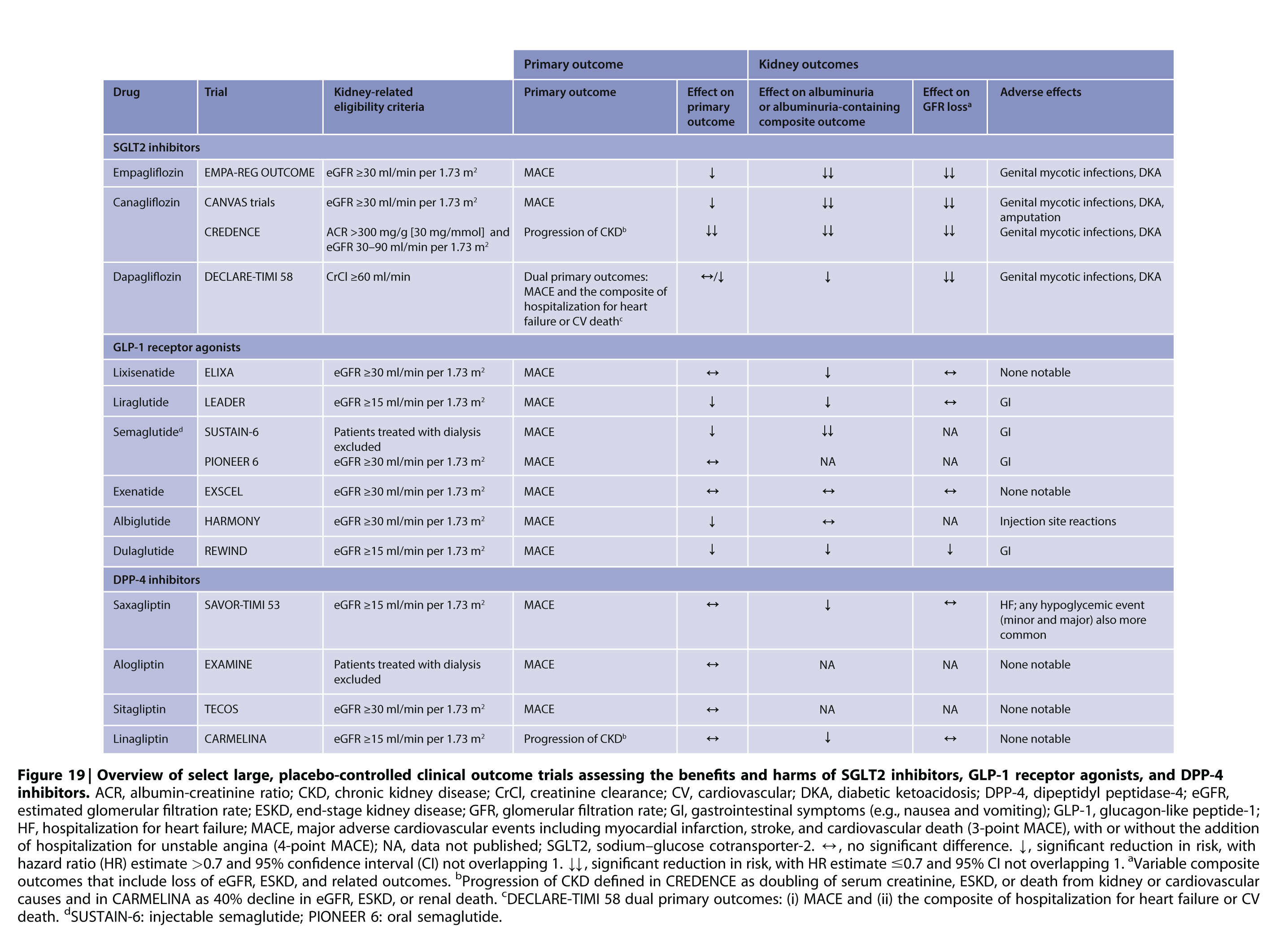
4.2 SODIUM-GLUCOSE COTRANSPORTER-2 INHIBITORS (SGLT2I)
Recommendation 4.2.1:
We recommend treating patients with T2D, CKD, and an eGFR ≥30 mL/min/1.73 m² with an SGLT2i (1A).
Based on DAPA-CKD and the forthcoming EMPA-KIDNEY trial, the GFR threshold at which SGLT2i can be initiated will be reassessed in future guideline updates.
Please click here to view the 'Sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors (SGLT2I):' flow chart

2.1. GLYCEMIC MONITORING
Recommendation 2.1.1:
We recommend using hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) to monitor glycemic control in patients with diabetes and CKD (1C).
Please click here to view the 'Glycemic monitoring' flow chart
4. ANTIHYPERGLYCEMIC THERAPIES IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES (T2D) AND CKD
Practice Point 4.3:
Patient preferences, comorbidities, eGFR, and cost should guide selection of additional drugs to manage glycemia, when needed, with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) generally preferred.
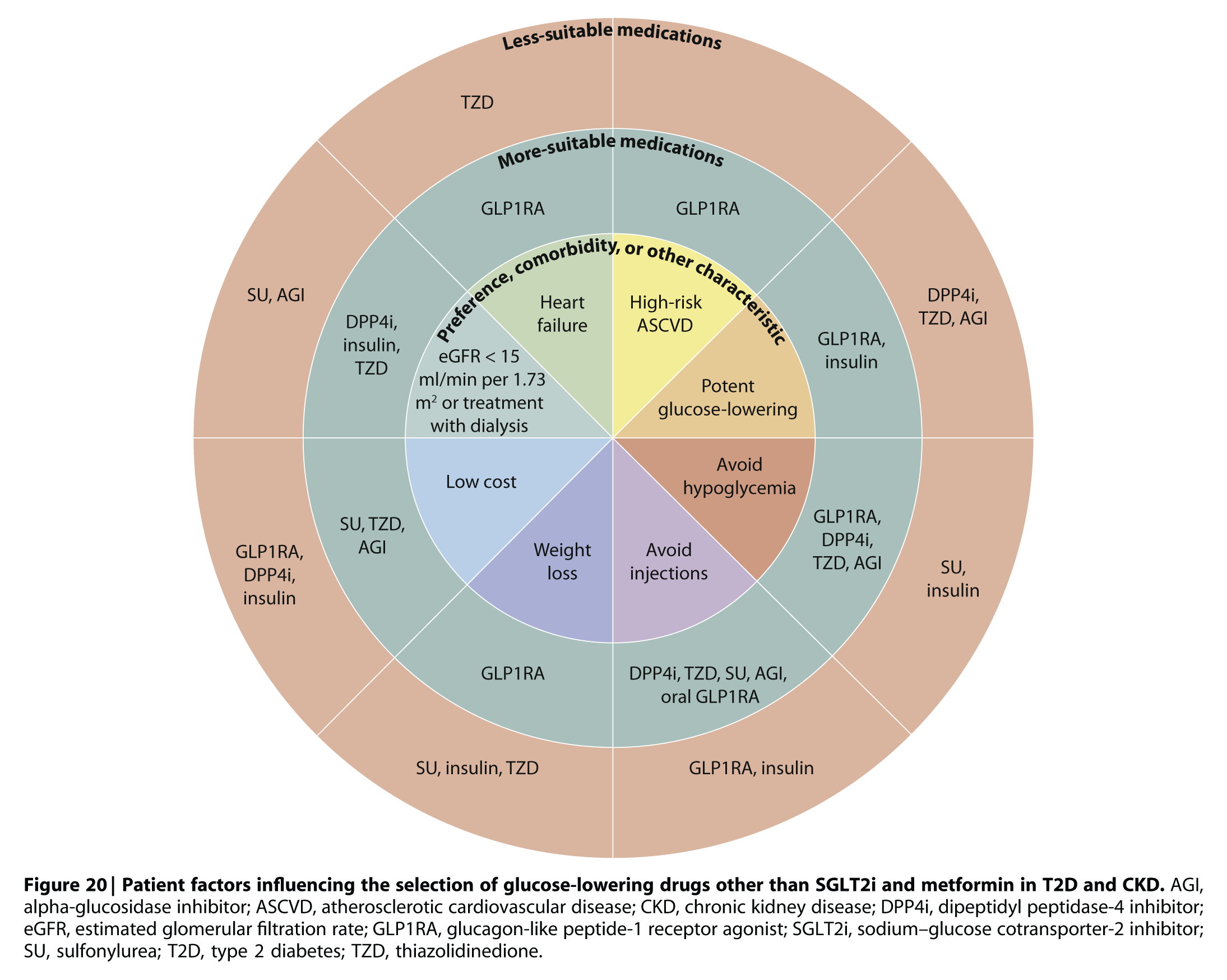
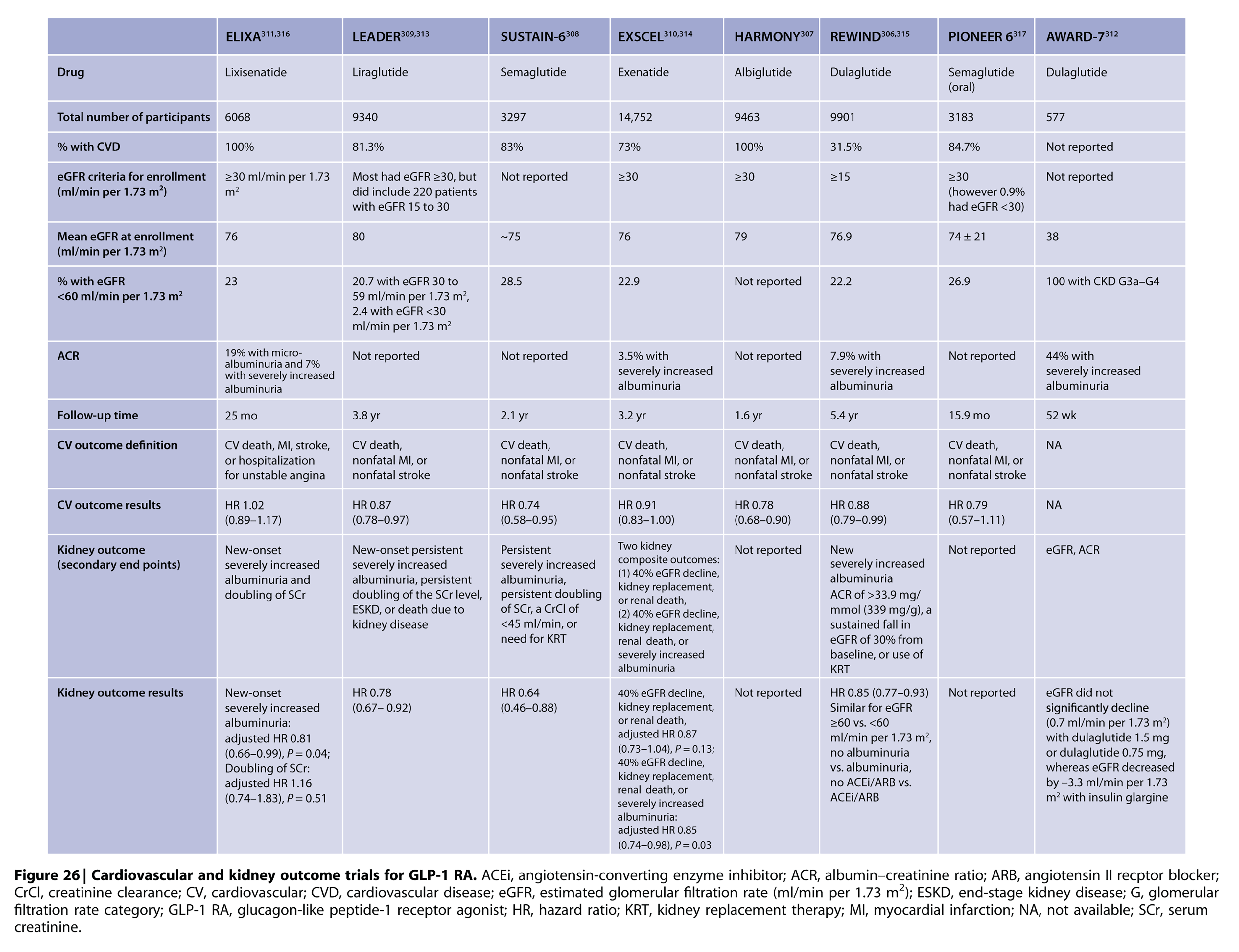
4.3 GLUCAGON-LIKE PEPTIDE-1 RECEPTOR AGONISTS (GLP-1 RA)
Recommendation 4.3.1:
In patients with T2D and CKD who have not achieved individualized glycemic targets
despite use of metformin and SGLT2i, or who are unable to use those medications, we recommend a long-acting GLP-1 RA (1B).
Please click here to view the 'Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1 RA)' flow chart
5.1. SELF-MANAGEMENT EDUCATION PROGRAMS
Recommendation 5.1.1:
We recommend that a structured self-management educational program be implemented for care of people with diabetes and CKD (1C).
5.2. TEAM-BASED INTEGRATED CARE
Recommendation 5.2.1:
We suggest that policymakers and institutional decision-makers implement team-based, integrated care focused on risk evaluation and patient empowerment to provide comprehensive care in patients with diabetes and CKD (2B).
Please click here to view the 'Patient education and team-based integrated care' flow chart